German scientists detected viral DNA in monkeypox patient’s rooms, but caution that surface contamination with virus DNA or viable virus does not prove that infection can occur after contact with the surfaces. During the currently evolving outbreak of monkeypox cases outside of known endemic area
, transmission is mostly driven by close physical contact with symptomatic people. While viral transmission between humans has been described previously, data on environmental contamination of surfaces is very limited.
Monkeypox is a zoonotic disease, i.e. it can be transmitted between animals and humans via direct or indirect contacts. Following the eradication of smallpox and the end of universal smallpox vaccination, monkeypox is currently the most prevalent orthopoxvirus infection in humans.In a new study, Nörz et al. swabbed surfaces in the immediate and adjacent rooms of two hospitalized monkeypox patients in Germany.
According to the authors, all the surfaces that the two patients had touched directly showed viral contamination, with the highest loads detected in both bathrooms . Fabrics such as towels, shirts, or pillowcases that the patients used frequently also showed viral contamination.The authors highlight that there currently are no definite data on what dose of virus leads to infection with monkeypox in humans.
Prevention of virus spread from symptomatic patients should be individually adapted. Based on their findings, the authors conclude that “regular disinfection of frequent hand and skin contact points during the care processes additional to regular room cleaning and surface disinfection using products with at least virucidal activity against enveloped viruses can reduce infectious virus on surfaces and thereby risk of nosocomial transmission.
Reference: “Evidence of surface contamination in hospital rooms occupied by patients infected with monkeypox, Germany, June 2022 separator commenting unavailable ” by Dominik Nörz, Susanne Pfefferle, Thomas T. Brehm, Gefion Franke, Ilka Grewe, Birte Knobling, Martin Aepfelbacher, Samuel Huber, Eva M. Klupp, Sabine Jordan, Marylyn M. Addo, Julian Schulze zur Wiesch, Stefan Schmiedel, Marc Lütgehetmann and Johannes K.
Indonesia Berita Terbaru, Indonesia Berita utama
Similar News:Anda juga dapat membaca berita serupa dengan ini yang kami kumpulkan dari sumber berita lain.
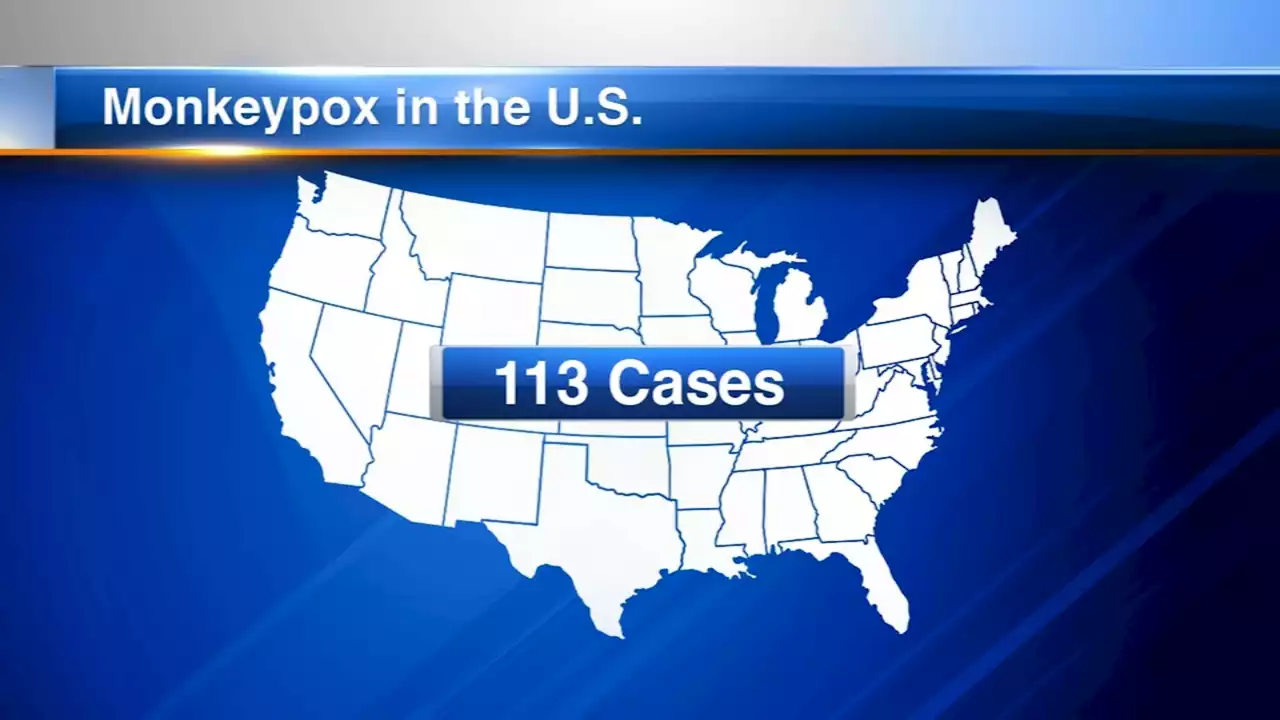 Wisconsin reports 1st confirmed case of monkeypox virusThe health department said the risk of infection remains low for the general public.
Wisconsin reports 1st confirmed case of monkeypox virusThe health department said the risk of infection remains low for the general public.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Bad News, Boys! Vaping Linked to Erectile DysfunctionScientists have discovered yet another reason why vaping sucks.
Bad News, Boys! Vaping Linked to Erectile DysfunctionScientists have discovered yet another reason why vaping sucks.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Scientists discovered a terrifying new species of hairy crab in Western AustraliaScientists have discovered a new species of hairy crab off the coast of Western Australia, and it's pretty terrifying.
Scientists discovered a terrifying new species of hairy crab in Western AustraliaScientists have discovered a new species of hairy crab off the coast of Western Australia, and it's pretty terrifying.
Baca lebih lajut »
 NYC and DC run out of monkeypox vaccinesNew York City and Washington, D.C., ran out of vaccines for monkeypox shortly after the cities implemented an online portal patients could use to schedule their shots.
NYC and DC run out of monkeypox vaccinesNew York City and Washington, D.C., ran out of vaccines for monkeypox shortly after the cities implemented an online portal patients could use to schedule their shots.
Baca lebih lajut »
 WHO: Monkeypox not a serious threat at the momentMonkeypox may be spreading across dozens of nations, but doesn’t qualify as a global health emergency yet, the World Health Organization said Saturday.
WHO: Monkeypox not a serious threat at the momentMonkeypox may be spreading across dozens of nations, but doesn’t qualify as a global health emergency yet, the World Health Organization said Saturday.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Wisconsin Reports First Confirmed Case of MonkeypoxHealth officials in Wisconsin say the state now has its first confirmed case of monkeypox. The Wisconsin Department of Health Services said Friday that a resident in Dane County is in isolation. The department said the risk of infection remains low for the general public. No further details about the patient were available. Most monkeypox patients experience only fever, body…
Wisconsin Reports First Confirmed Case of MonkeypoxHealth officials in Wisconsin say the state now has its first confirmed case of monkeypox. The Wisconsin Department of Health Services said Friday that a resident in Dane County is in isolation. The department said the risk of infection remains low for the general public. No further details about the patient were available. Most monkeypox patients experience only fever, body…
Baca lebih lajut »
