Astronomers spot over 20,000 supernovas every year, but this one stands out.
This new supernova is the closest to Earth in a decade. It's visible in the night sky right now.
Since Itagaki reported the observation to the International Astronomical Union that night, the brightening star in the Pinwheel Galaxy has become the most studied object in the night sky. Both the world's largest scientific telescopes and amateur skywatchers around the globe have turned their lenses toward the freshly exploded, which has since been declared the nearest supernova explosion in the last five years.
Daniel Perley, an astrophysicist at Liverpool John Moores University, told Space.com that thanks to the large quantity of available observations of the galaxy taken by both amateurs and professionals, astronomers might be able to pin down the exact moment of the explosion to within minutes. "Usually, when a supernova is found, it's already a day, two days, three days, even a week after the explosion when we first see it," Perley said."This one was found within hours of the actual initial explosion of the star, and we may even be able to get that down to a few minutes after we collect some of the amateur data that people have been incidentally taking of the galaxy.
With today's technology, supernova detections are not rare. According to Cardiff University astrophysicist Cosimo Inserra, powerful survey telescopes find several supernovas every night. Within a single year, more than 22,000 so-called transient events, sudden powerful brightenings in galaxies, can be discovered. This number includes supernovas, but also stars shredded by"On average, the distance of the majority of these transients is up to redshift 0.1," Inserra said.
Indonesia Berita Terbaru, Indonesia Berita utama
Similar News:Anda juga dapat membaca berita serupa dengan ini yang kami kumpulkan dari sumber berita lain.
 Astronomers race to observe rare supernova in a nearby galaxyAn exploding star spotted in the Pinwheel galaxy, 21 million light years from Earth, offers a rare chance to watch a supernova unfolding in real time
Astronomers race to observe rare supernova in a nearby galaxyAn exploding star spotted in the Pinwheel galaxy, 21 million light years from Earth, offers a rare chance to watch a supernova unfolding in real time
Baca lebih lajut »
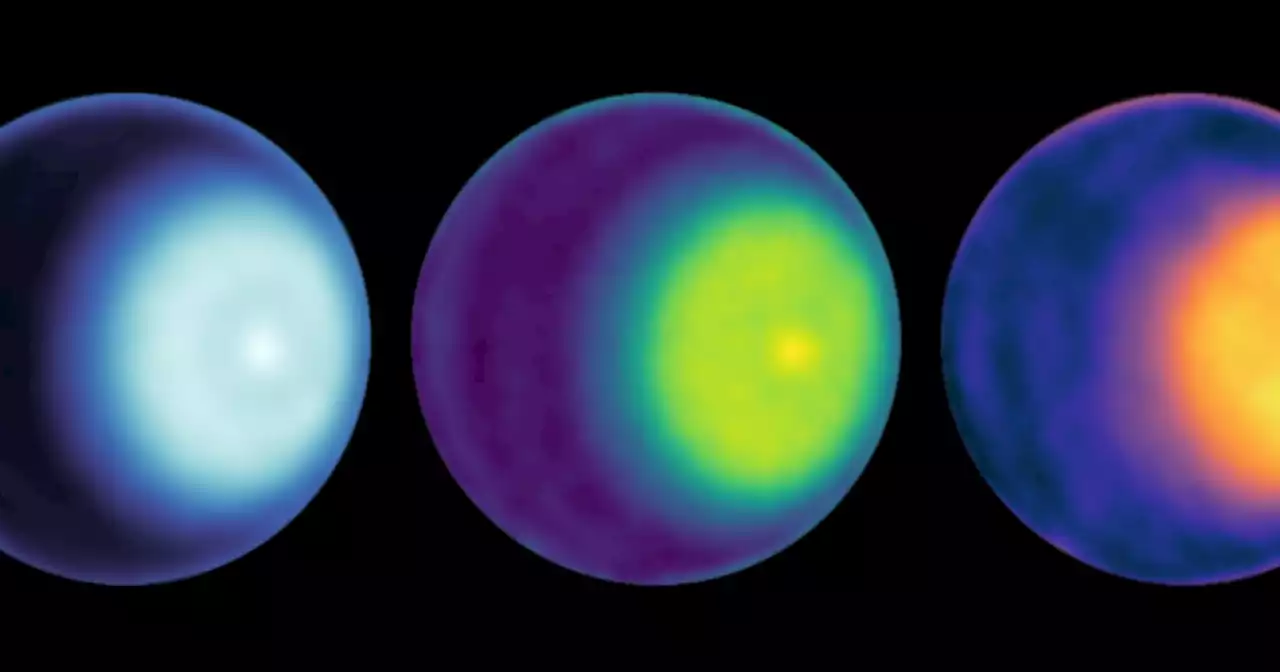 Astronomers spot cyclones at Uranus' pole for first time | Digital TrendsUranus is usually portrayed as a generally featureless blue ball, but when seen using radio telescopes, the pole reveals a swirling cyclone.
Astronomers spot cyclones at Uranus' pole for first time | Digital TrendsUranus is usually portrayed as a generally featureless blue ball, but when seen using radio telescopes, the pole reveals a swirling cyclone.
Baca lebih lajut »
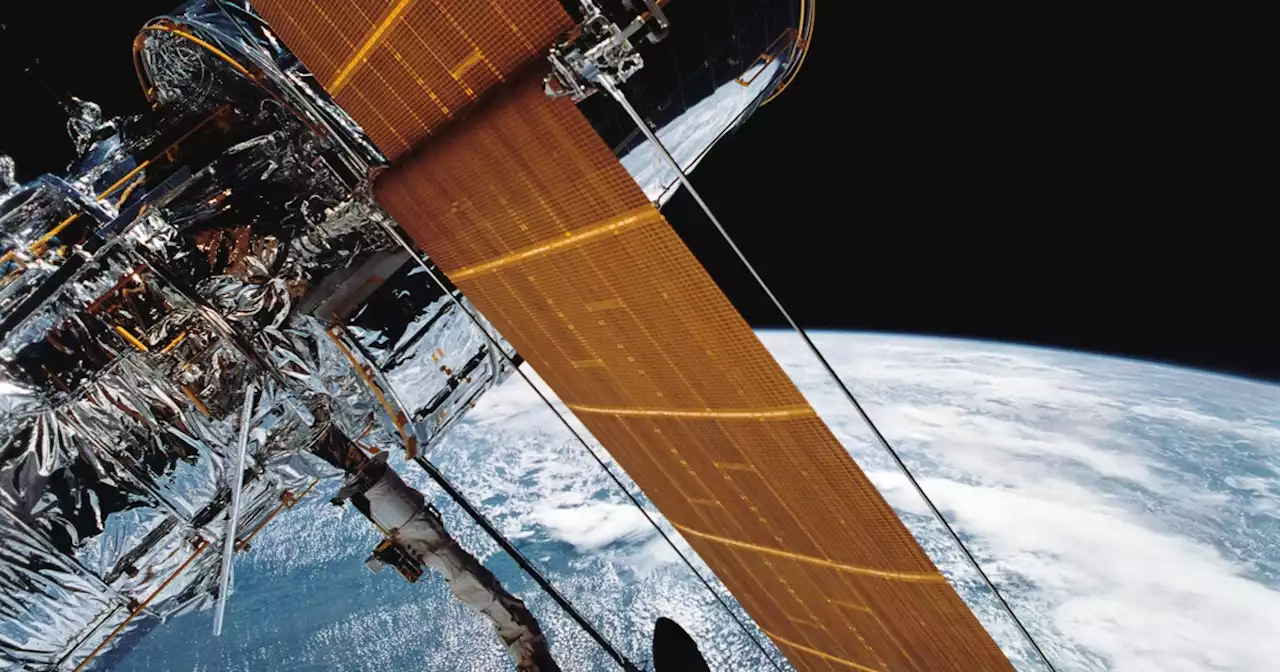 NASA's Hubble Space Telescope searching for black holeAstronomers are using a space telescope from NASA to search for a rare 'intermediate-sized' black hole that is estimated to be in a star cluster 6,000 light years away from Earth.
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope searching for black holeAstronomers are using a space telescope from NASA to search for a rare 'intermediate-sized' black hole that is estimated to be in a star cluster 6,000 light years away from Earth.
Baca lebih lajut »
 eROSITA Sees Changes in the Most Powerful QuasarAn international team of astronomers observed the quasar J1114 in the X-ray band for the first time, revealing things about its inner workings and quasars they shape their host galaxies.
eROSITA Sees Changes in the Most Powerful QuasarAn international team of astronomers observed the quasar J1114 in the X-ray band for the first time, revealing things about its inner workings and quasars they shape their host galaxies.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Uranus may be more active than scientists previously believedAstronomers using the Very Large Array have detected what could be a stormy vortex at Uranus' north pole, which could change everything.
Uranus may be more active than scientists previously believedAstronomers using the Very Large Array have detected what could be a stormy vortex at Uranus' north pole, which could change everything.
Baca lebih lajut »
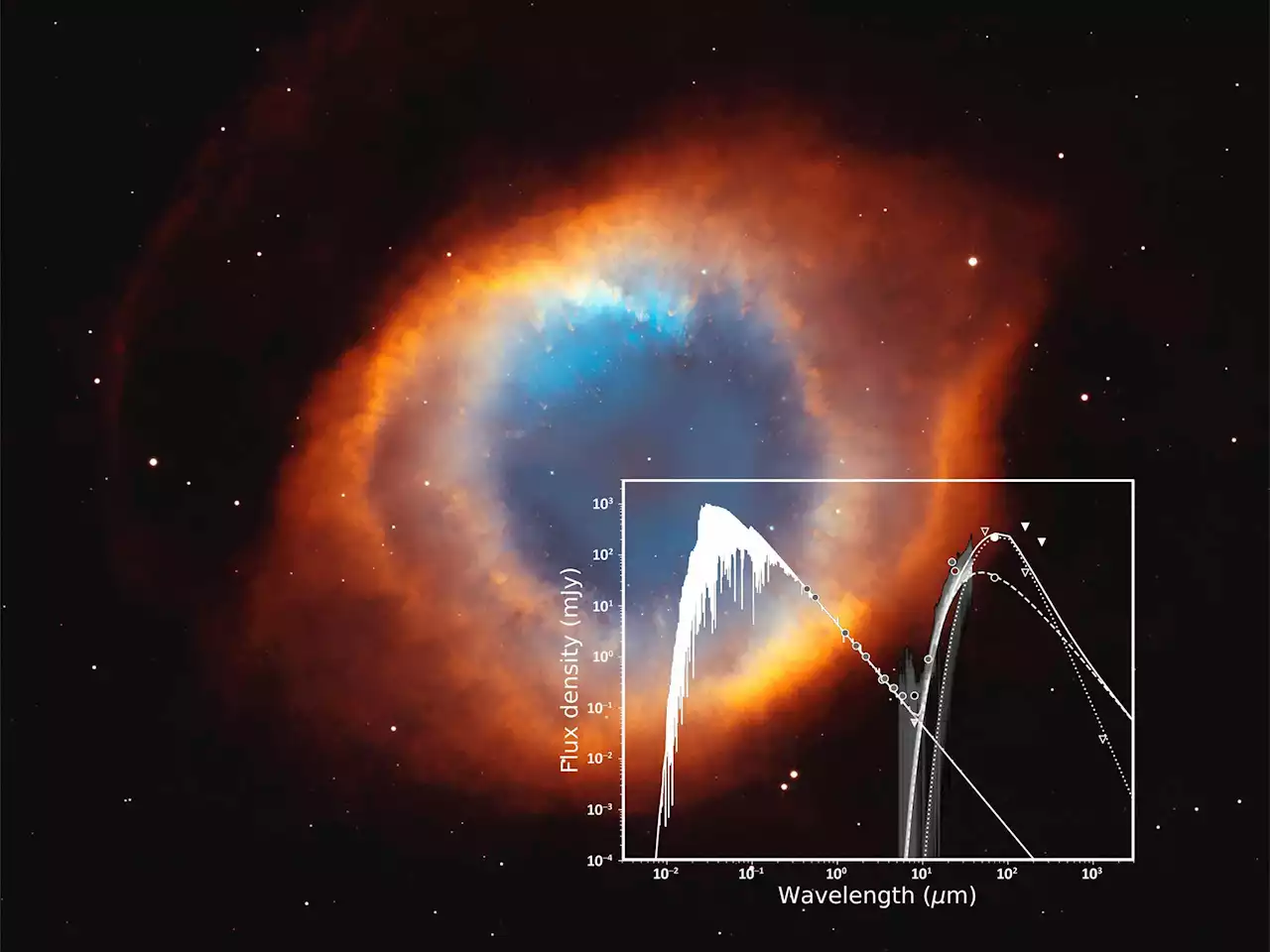 NASA Reveals a Destroyed Planetary SystemOnce a star evolves beyond the main sequence – the longest stage of stellar evolution, during which the radiation generated by nuclear fusion in a star’s core is balanced by gravitation – the fate of any planetary system it may have had is an enigma. Astronomers generally don’t know what happens to
NASA Reveals a Destroyed Planetary SystemOnce a star evolves beyond the main sequence – the longest stage of stellar evolution, during which the radiation generated by nuclear fusion in a star’s core is balanced by gravitation – the fate of any planetary system it may have had is an enigma. Astronomers generally don’t know what happens to
Baca lebih lajut »
