The Zhurong rover, part of China's Tianwen-1 Mars mission, has found evidence of liquid water at low Martian latitudes, indicating potentially habitable environments. This discovery, contradicting previous beliefs that water could only exist in solid or gaseous states on Mars, was made by analyzing
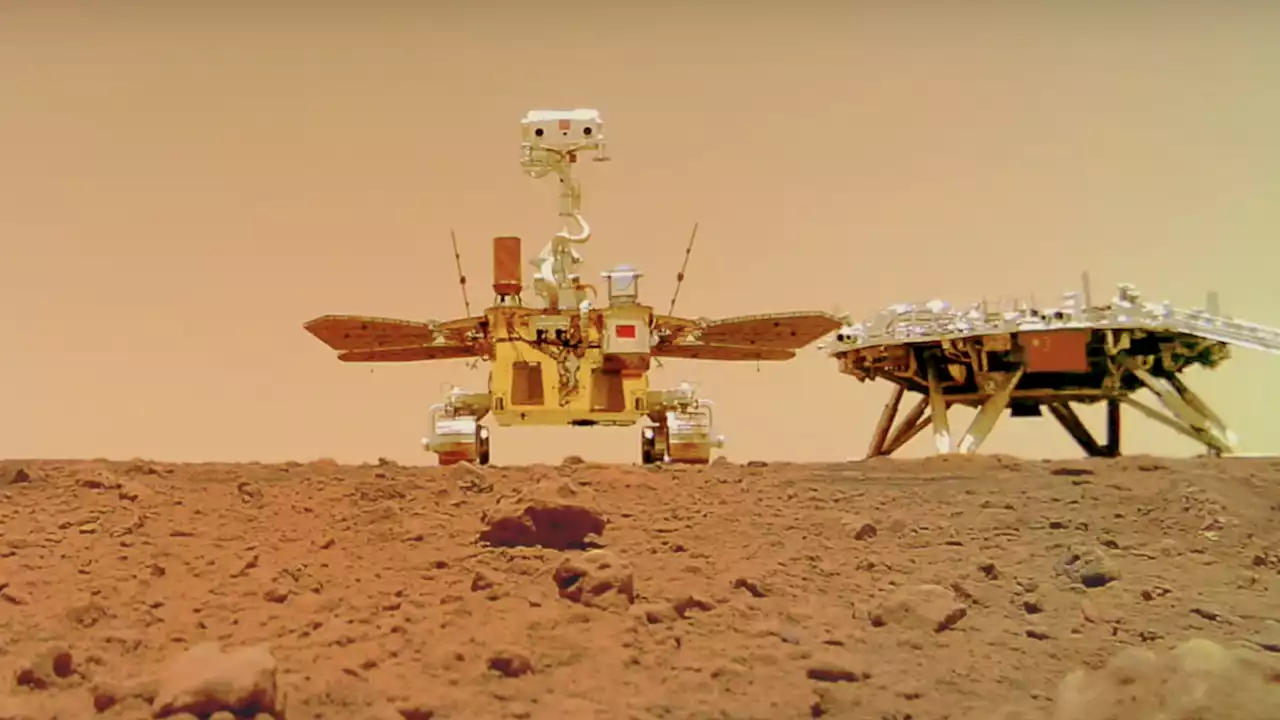
A selfie taken by the Zhurong rover alongside its landing platform, captured with a wireless camera. Credit: Chinese National Space Administrationmission, has found evidence of liquid water at low Martian latitudes, indicating potentially habitable environments. This discovery, contradicting previous beliefs that water could only exist in solid or gaseous states on Mars, was made by analyzing morphological features and mineral compositions of dunes in the landing area.
Previous studies have provided proof of a large amount of liquid water on early Mars, but with the escape of the early Martian atmosphere during the later period, the climate changed dramatically. Very low pressure and water vapor content make it difficult for liquid water to sustainably exist on Mars today. Thus, it has been widely believed that water can only exist there in solid or gaseous forms.
The researchers used data obtained by the Navigation and Terrain Camera , the Multispectral Camera , and the Mars Surface Composition Detector aboard the Zhurong rover to study the different-scale surface features and material compositions of dunes in the landing area. Specifically, salts in dunes cause frost/snow to melt at low temperatures to form salty liquid water. When the saline water dries, the precipitated hydrated sulfate, opal, iron oxide, and other hydrated minerals cement sand particles to form sand aggregates and even crust. Then the crust is further cracked by shrinkage. The later frost/snow melting process further forms polygonal ridges and a strip-like trace on the crust surface.
Indonesia Berita Terbaru, Indonesia Berita utama
Similar News:Anda juga dapat membaca berita serupa dengan ini yang kami kumpulkan dari sumber berita lain.
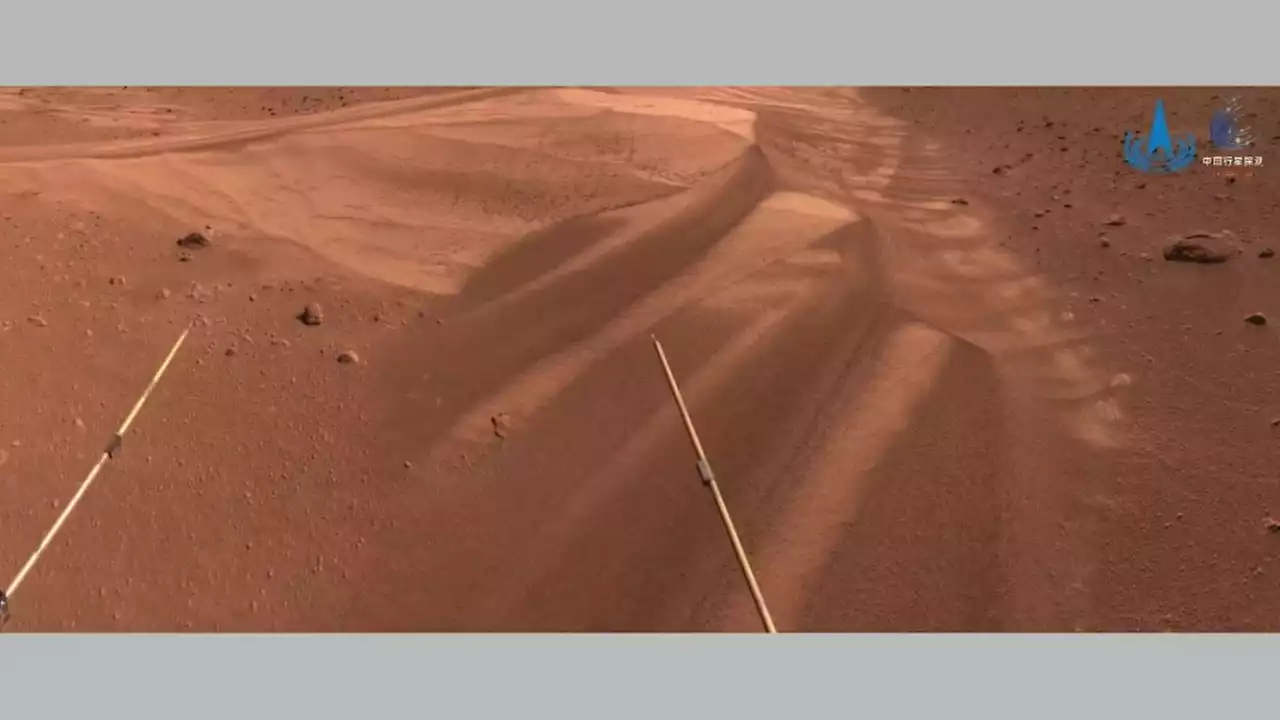 China's Zhurong Mars rover finds signs of recent water activity on Red PlanetMartian water played a major role in creating intriguing surface features on miniature sand dunes, scientists say.
China's Zhurong Mars rover finds signs of recent water activity on Red PlanetMartian water played a major role in creating intriguing surface features on miniature sand dunes, scientists say.
Baca lebih lajut »
 China's Mars Zhurong rover could be dead, but its legacy will live onChina recently confirmed that its first Mars rover, Zhurong, may be dead due to an accumulation of Martian dust on its solar panels.
China's Mars Zhurong rover could be dead, but its legacy will live onChina recently confirmed that its first Mars rover, Zhurong, may be dead due to an accumulation of Martian dust on its solar panels.
Baca lebih lajut »
 China's Mars rover finds signs of recent water in sand dunesA new study suggests water on Mars may be more widespread and recent than previously thought. Scientists reported the finding from China's Mars rover in Science Advances on Friday. The rover spotted cracks and crusts in the Martian salt-rich dunes. Small pockets of water from thawing frost or snow, mixed with salt, likely resulted in the cracked surface. The six-wheeled rover was launched in 2020 and arrived at Mars in 2021. It spent a year roaming the Martian surface before going into hibernation. It's yet to wake up, after almost a year. Researchers say the rover's solar panels are likely covered with dust, choking off its power source.
China's Mars rover finds signs of recent water in sand dunesA new study suggests water on Mars may be more widespread and recent than previously thought. Scientists reported the finding from China's Mars rover in Science Advances on Friday. The rover spotted cracks and crusts in the Martian salt-rich dunes. Small pockets of water from thawing frost or snow, mixed with salt, likely resulted in the cracked surface. The six-wheeled rover was launched in 2020 and arrived at Mars in 2021. It spent a year roaming the Martian surface before going into hibernation. It's yet to wake up, after almost a year. Researchers say the rover's solar panels are likely covered with dust, choking off its power source.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Rover Spots Possible Evidence of Liquid Water on Modern MarsHydrated dunes suggest water can persist on some parts of the Martian surface, according to data from China's troubled Zhurong rover.
Rover Spots Possible Evidence of Liquid Water on Modern MarsHydrated dunes suggest water can persist on some parts of the Martian surface, according to data from China's troubled Zhurong rover.
Baca lebih lajut »
 China’s Rover May Have Found Hints of Water on Mars DunesChina’s Zhurong Mars rover has seen better days, but it did make a groundbreaking discovery.
China’s Rover May Have Found Hints of Water on Mars DunesChina’s Zhurong Mars rover has seen better days, but it did make a groundbreaking discovery.
Baca lebih lajut »
 It may have been snowing on Mars 400,000 years agoChina’s Zhurong rover has found evidence for liquid water on the surface of Mars - and it probably began as snow or frost that melted into sand dunes
It may have been snowing on Mars 400,000 years agoChina’s Zhurong rover has found evidence for liquid water on the surface of Mars - and it probably began as snow or frost that melted into sand dunes
Baca lebih lajut »
