The wolf genomes could help settle the long-standing mystery of dog domestication.
Roughly 30,000 to 15,000 years ago, the first dogs emerged from gray wolves. Exactly when, where, and how this monumental event occurred isn’t known. For decades, geneticists and evolutionary biologists have been unable to come to a consensus on the long-standing mystery. However, a studyAn international group of collaborators analyzed 72 genomes of ancient wolves from Europe, Siberia, and North America and compared them with modern wolves, as well as modern and ancient dogs.
On the whole, dogs were more closely related to ancient wolves from Asia than from Europe, says Anders Bergström, a geneticist at the Francis Crick Institute in London who co-authored the paper. But, he adds, “We also find that it gets a little more complex.” “While we do make some progress on where dogs fit into the wolf puzzle, we still haven’t solved the question of dog origins,” Bergström says. “The range of possibilities for where dogs came from is still quite large.”
Indonesia Berita Terbaru, Indonesia Berita utama
Similar News:Anda juga dapat membaca berita serupa dengan ini yang kami kumpulkan dari sumber berita lain.
 Directed evolution and selection of biostable l-DNA aptamers with a mirror-image DNA polymerase - Nature BiotechnologyMirror-image PCR and l-DNA sequencing-by-synthesis enable the directed evolution and selection of functional l-DNA aptamers.
Directed evolution and selection of biostable l-DNA aptamers with a mirror-image DNA polymerase - Nature BiotechnologyMirror-image PCR and l-DNA sequencing-by-synthesis enable the directed evolution and selection of functional l-DNA aptamers.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Ghost DNA from hybrid coyotes could save endangered red wolvesA hidden reservoir of red wolf DNA has been found in coyotes in southwestern Louisiana – and it could be used to help the endangered wolves grow their wild population
Ghost DNA from hybrid coyotes could save endangered red wolvesA hidden reservoir of red wolf DNA has been found in coyotes in southwestern Louisiana – and it could be used to help the endangered wolves grow their wild population
Baca lebih lajut »
 Dogs are descended from two populations of ancient wolvesThe story of when and where dogs were domesticated is still shrouded in mystery. A new study of ancient DNA shows that modern dogs are more closely related to wolves from Asia – but another group of wolves from Europe has also contributed to their ancestry
Dogs are descended from two populations of ancient wolvesThe story of when and where dogs were domesticated is still shrouded in mystery. A new study of ancient DNA shows that modern dogs are more closely related to wolves from Asia – but another group of wolves from Europe has also contributed to their ancestry
Baca lebih lajut »
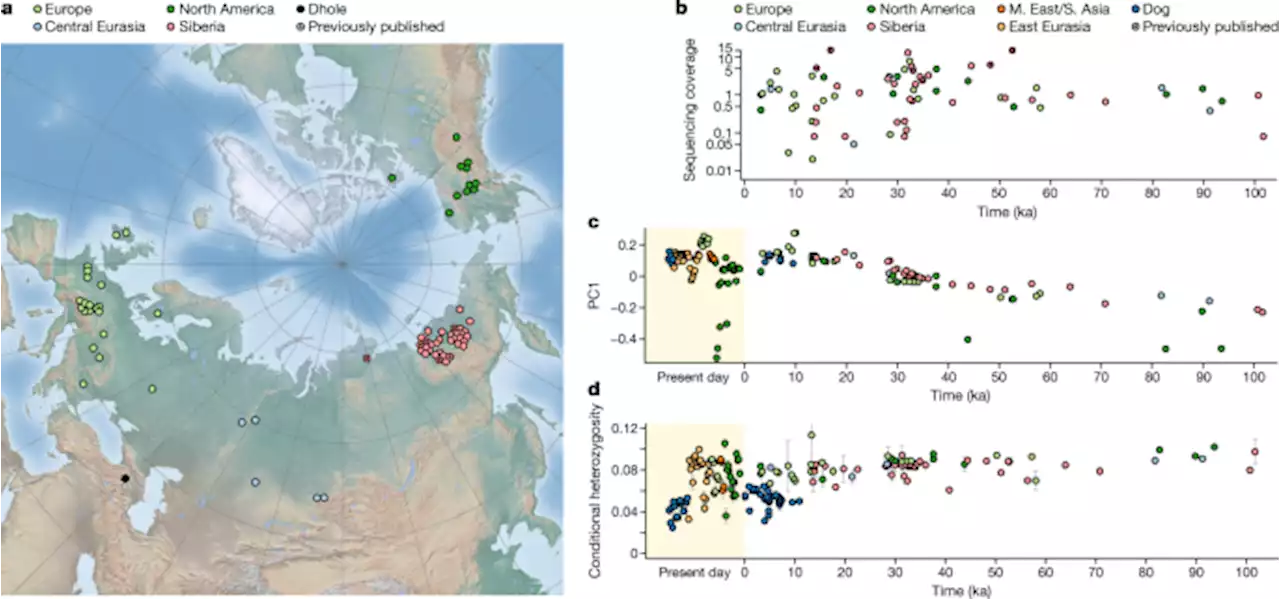 Grey wolf genomic history reveals a dual ancestry of dogs - NatureDNA from ancient wolves spanning 100,000 years sheds light on wolves’ evolutionary history and the genomic origin of dogs.
Grey wolf genomic history reveals a dual ancestry of dogs - NatureDNA from ancient wolves spanning 100,000 years sheds light on wolves’ evolutionary history and the genomic origin of dogs.
Baca lebih lajut »
