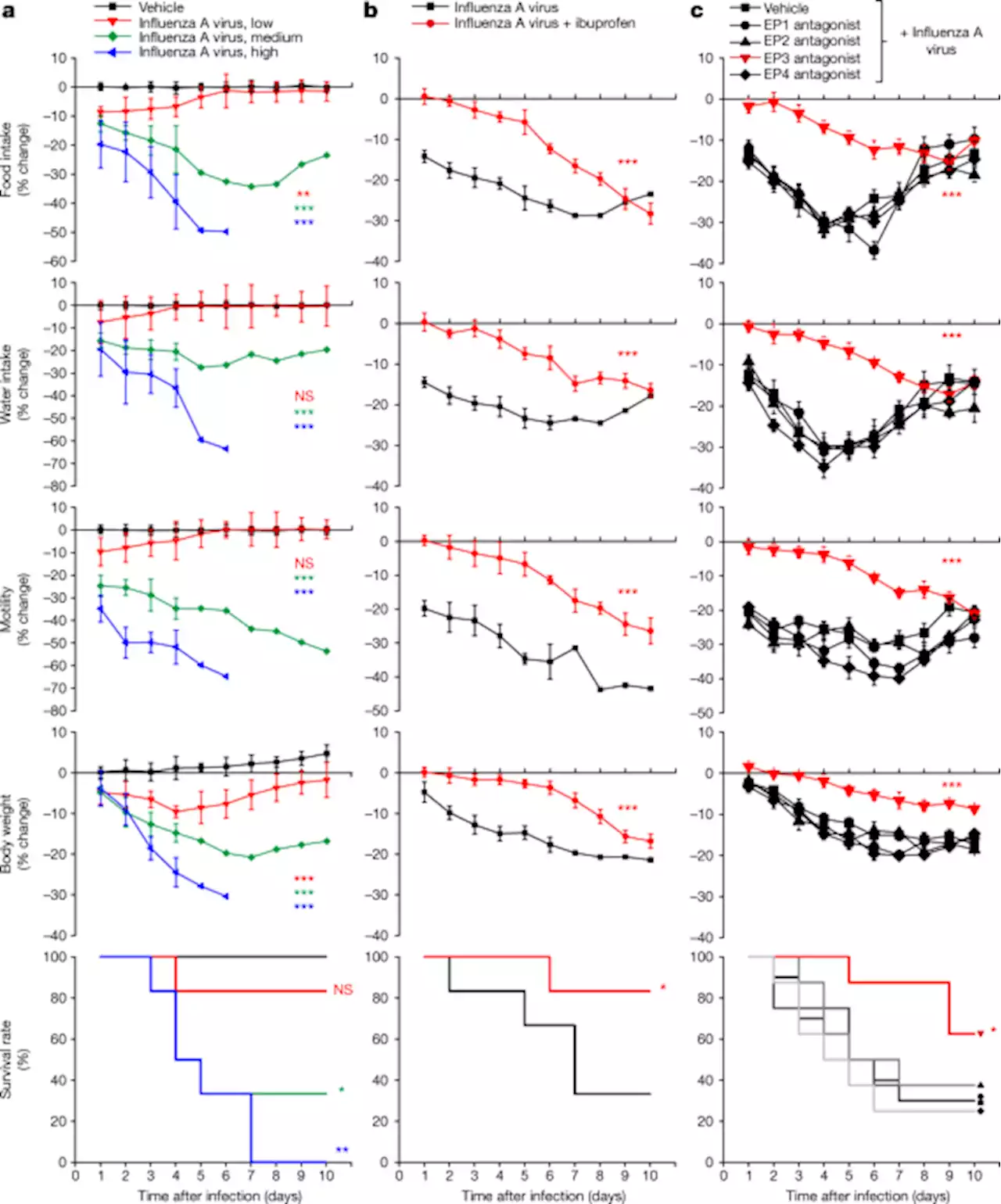
Nature research paper: An airway-to-brain sensory pathway mediates influenza-induced sickness
) or diphtheria toxin supplemented with 0.05% Fast Green FCF Dye using a sharply pulled glass pipette attached to a Nanoject Injector . AAV-cre , AAV-flex-tdTomato , AAV-GFP , and AAV-flex-AP were purchased. Successful injection was verified by Fast Green FCF Dye slowly filling the entire ganglion without leakage. Surgical wounds were closed with coated VICRYL Sutures and animals received Buprenorphine SR as an analgesic.
heparin, 1× Denhardt’s solution, 10% dextran sulfate), probe wash buffer , amplification buffer , and fluorophore-labelled HCR amplifiers were purchased from Molecular Instruments. NJP ganglia were freshly collected, mounted in OCT and cryosectioned . Tissue was post-fixed , washed , treated with 1% hydrogen peroxide , and incubated withHCR probes .
Indonesia Berita Terbaru, Indonesia Berita utama
Similar News:Anda juga dapat membaca berita serupa dengan ini yang kami kumpulkan dari sumber berita lain.
 Visible light-exposed lignin facilitates cellulose solubilization by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases - Nature CommunicationsDegradation of plant biomass, comprised of cellulose and polyaromatic lignin, is promoted by light. Here, the authors show that light promotes lignin-catalyzed generation of hydrogen peroxide, which is used by redox enzymes to degrade cellulose.
Visible light-exposed lignin facilitates cellulose solubilization by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases - Nature CommunicationsDegradation of plant biomass, comprised of cellulose and polyaromatic lignin, is promoted by light. Here, the authors show that light promotes lignin-catalyzed generation of hydrogen peroxide, which is used by redox enzymes to degrade cellulose.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Dollar General reformulates and rebrands its cat and dog food line Nature’s MenuDollar General Corp. said Tuesday it has reformulated and rebranded its dog and cat food line, Nature’s Menu. The company said its pet food is available...
Dollar General reformulates and rebrands its cat and dog food line Nature’s MenuDollar General Corp. said Tuesday it has reformulated and rebranded its dog and cat food line, Nature’s Menu. The company said its pet food is available...
Baca lebih lajut »
 Future warming from global food consumption - Nature Climate ChangeAlthough the role of the human diet in climate change has been widely acknowledged, current practices fail to capture its realistic effect on warming. In this Analysis, Ivanovich et al. develop a global food consumption emission inventory and estimate the associated future climate impact using a reduced-complexity climate model.
Future warming from global food consumption - Nature Climate ChangeAlthough the role of the human diet in climate change has been widely acknowledged, current practices fail to capture its realistic effect on warming. In this Analysis, Ivanovich et al. develop a global food consumption emission inventory and estimate the associated future climate impact using a reduced-complexity climate model.
Baca lebih lajut »
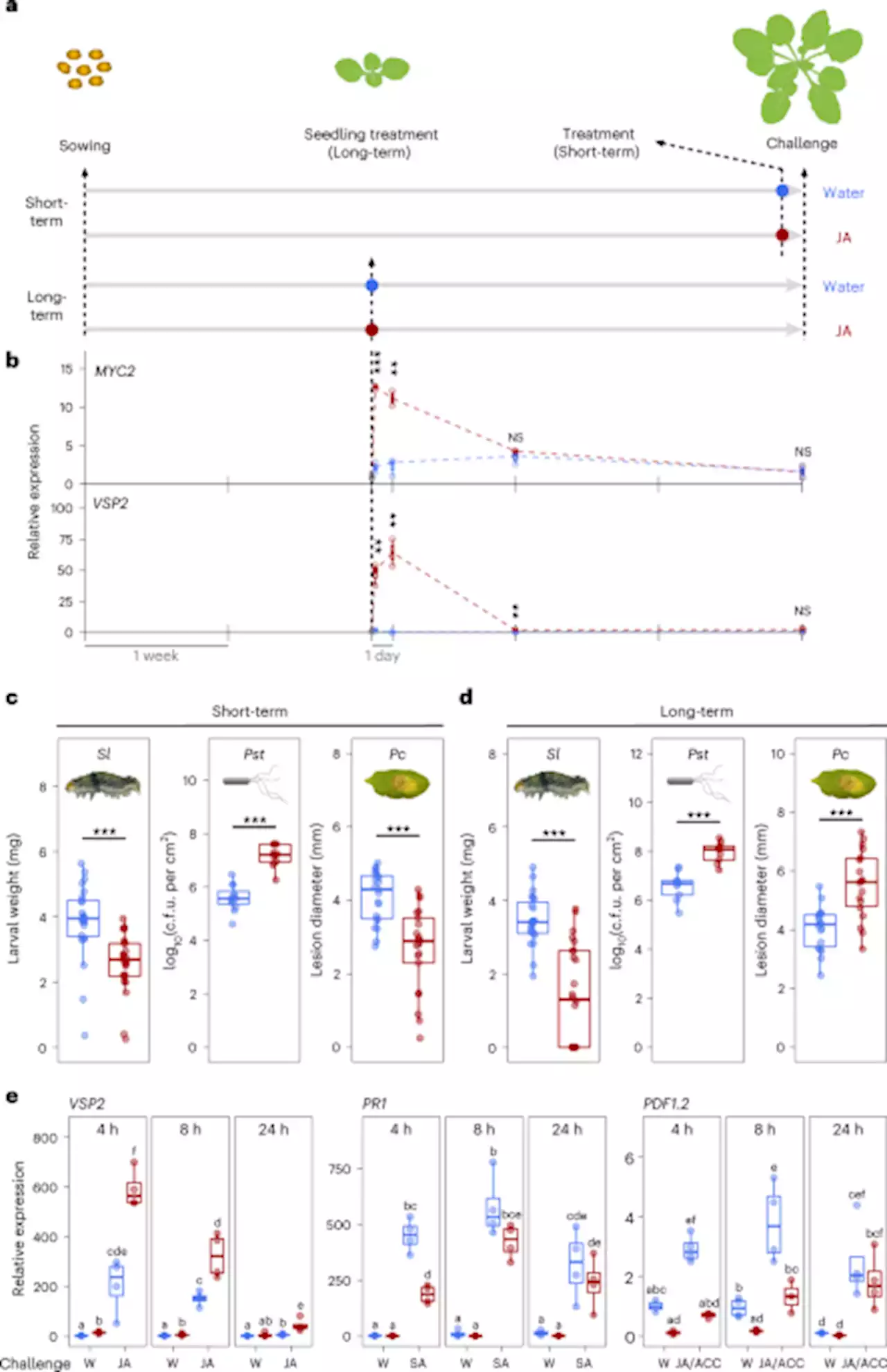 Long-lasting memory of jasmonic acid-dependent immunity requires DNA demethylation and ARGONAUTE1 - Nature PlantsJasmonic acid (JA) is involved in defence against herbivores. Once the plant is attacked, the memory of aggression can linger for weeks, including in newly formed leaves. The authors investigate what the induced changes in the transcriptome and methylome are, and uncouple short- and long-term effects of JA.
Long-lasting memory of jasmonic acid-dependent immunity requires DNA demethylation and ARGONAUTE1 - Nature PlantsJasmonic acid (JA) is involved in defence against herbivores. Once the plant is attacked, the memory of aggression can linger for weeks, including in newly formed leaves. The authors investigate what the induced changes in the transcriptome and methylome are, and uncouple short- and long-term effects of JA.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Shoot the messenger: RNA editing is here - Nature BiotechnologyRNA editing is rapidly gaining prominence as its transient and reversible changes promise a safer and more flexible option to reverse disease-causing mutations than DNA editing.
Shoot the messenger: RNA editing is here - Nature BiotechnologyRNA editing is rapidly gaining prominence as its transient and reversible changes promise a safer and more flexible option to reverse disease-causing mutations than DNA editing.
Baca lebih lajut »
 Faunal engineering stimulates landscape-scale accretion in southeastern US salt marshes - Nature CommunicationsThe contribution of animal ecosystem engineers to coastal geomorphological processes is often neglected. Here, the authors combine observational, experimental and modelling work to demonstrate that ecosystem engineering by mussels is a much stronger driver of salt marsh accretion rates than expected.
Faunal engineering stimulates landscape-scale accretion in southeastern US salt marshes - Nature CommunicationsThe contribution of animal ecosystem engineers to coastal geomorphological processes is often neglected. Here, the authors combine observational, experimental and modelling work to demonstrate that ecosystem engineering by mussels is a much stronger driver of salt marsh accretion rates than expected.
Baca lebih lajut »